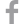Air Emissions (GHG And Others)
At Qatar Steel, we are committed to reducing our air emissions, and particularly our GHG emissions, as outlined in our sustainability roadmap. A crucial initial phase towards effective GHG management entails precise identification, measurement, and monitoring of our emissions.
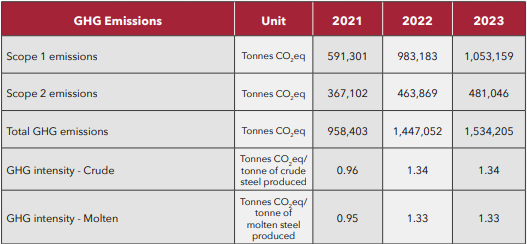
GHG EMISSIONS
It is important to note that Qatar Steel distinguishes itself from most international steel manufacturers by using natural gas as an energy source for steel production. This is a cleaner and more environmentally friendly alternative to the conventional method of coal burning.
In line with the QatarEnergy GHG Accounting and Reporting Programme, our approach involves managing and reporting GHG emissions as carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2eq) for Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions. This framework aligns with the European Union Monitoring and Reporting Regulation (MRR2012), ensuring consistency and adherence to international standards.
Scope 1 emissions encompass direct emissions resulting from fuel combustion (natural gas and flaring) and from emissions that take place in our processes. Emissions due to combustion of natural gas and flared gas are calculated using emission factors derived from the gas characteristics which we periodically analyse. The gasses included in the calculations are CO2, CH4 and N2O from Natural Gas combustion, materials and process emissions. Scope 2 emissions cover indirect emissions arising from the consumption of electricity. These emissions are calculated using emission factors provided by QatarEnergy for Kahramaa.
To ensure the credibility of our GHG report and verification, QatarEnergy has entrusted SGS, UK as the third-party verifier. We are pleased to announce that Qatar Steel has successfully completed the verification process in April 2023 and obtained the Scope 1 and Scope 2 verification statement in May 2023 (please click here or visit https://www.qatarsteel.com.qa).
Furthermore, to participate in the worldsteel CO2 emissions data collection programme, Qatar Steel submits CO2 emission monitoring data to worldsteel annually. In year 2022, we received a recognition for our 15-year participation in the “Worldsteel Climate Action Data Collection Programme” as climate action data provider.
The average GHG emissions from Scope 1 and Scope 2 in 2023 were around ~1.34 tons CO2eq/ ton of crude steel produced which is below the world average of 1.91 tons CO2eq/ ton of crude steel produced6 which includes different steel making routes combined such as BF-BOF, DRI-EAF and Scrap-EAF. Even when comparing our intensity to the global average for DRI-EAF route which is equal to 1.37 tons CO2eq/ ton of crude steel produced6, Qatar Steel’s value is still lower. (according to the World Steel Association Report – 2023 report).This notable increase can be attributed to the rise in production levels, primarily at the energy-intensive DR2 facility, which heavily relies on natural gas combustion. The reporting of GHG intensity at Qatar Steel is based on the World Steel Association frameworks, which employ the total production of crude steel as the denominator.
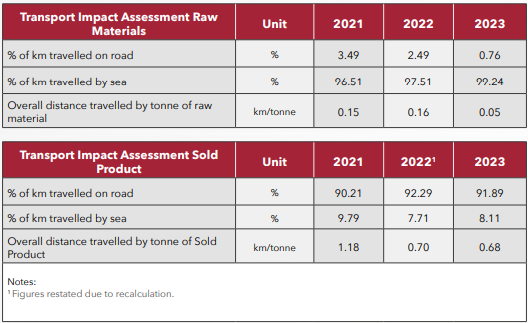
Currently, we are actively evaluating the impact of transportation resulting from our production, including both procurement of raw materials and shipping of finished products. To do so, we analyse the percentage of transport taken place via sea or road, while also evaluating our environmental footprint in terms of kilometres per tonne of material. The data is verified by third party auditor CARES on annual basis to issue EPD certificate for rebar.
Qatar Steel conducted pre-feasibility studies focused on exploring and evaluating various initiatives aimed at reducing its Scope 1 carbon emissions.In 2023, Qatar Steel collaborated with QatarEnergy to complete the CBAM model for calculating Specific Embedded Emissions (SEE) in accordance with CBAM requirements which will give an opportunity to export QS products in European market.
Currently, Qatar Steel is actively engaged in formulating the Monitoring Methodology Documentation (MMD) to meet the specifications outlined by CBAM. Qatar Steel also participated in Environmental Sustainability workshop organised by QatarEnergy in 2023.
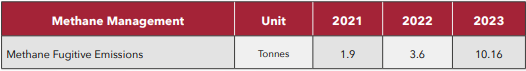
Methane management
To effectively manage and reduce the fugitive emissions, Qatar Steel has implemented a comprehensive programme focused on monitoring and controlling natural gas losses. Methane emissions and leak detection and repair (LDAR) findings provide valuable insights into the emission reduction achieved through equipment repairs and allows us to map new losses. The increased detection value of fugitive emissions in 2023 compared to the first period of implementation of LDAR, highlights the efficiency of the programme. Every year Qatar Steel conducts LDAR surveys, initiated by a third-party, to monitor components for leaks and repair detected leaks within a specified time frame. The last survey was performed in February 2024. This monitoring extends to all potentially leaking equipment, including valves, pumps, flanges, and connectors and is followed by a maintenance campaign aiming at reducing or eliminating such losses. The final maintenance survey report, which includes methane emissions and LDAR findings, provides valuable insights into the emission reduction achieved through equipment repairs and mapping of new sources of leaks.
OTHER AIR EMISSIONS
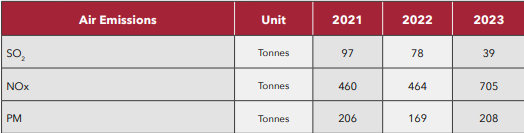
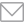
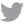
Significant air emissions for Qatar Steel, as listed on our CTO, are those of sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM). These emissions primarily result from the combustion of natural gas. To effectively assess and control these environmental emissions, we conduct regular monitoring activities. The monitoring procedures employed include Ambient Air Quality Monitoring System, monthly assessments of ambient air quality at various locations conducted by a third-party entity, utilisation of Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS), and manual stacks monitoring.
To mitigate the impact of emissions, we have implemented pollution control measures across all emission sources. These measures involve the use of bag house filters at EAFs and lime kilns, cyclone dust collectors, and wet scrubbers at DR Plants. Additionally, the company has established control units to address fugitive emissions, such as conveyor belts, hoppers, and suction hoods.
In 2023, Qatar Steel witnessed an increase in PM emissions due to increased production levels. Notably, NOx emissions have surged by 52%. Despite this, the company has successfully reduced SO2 emissions by more than 50%.. However, the company successfully managed to reduce SO2 emissions by more than 50%.